Detailed B-tree and B+tree index algorithm principle
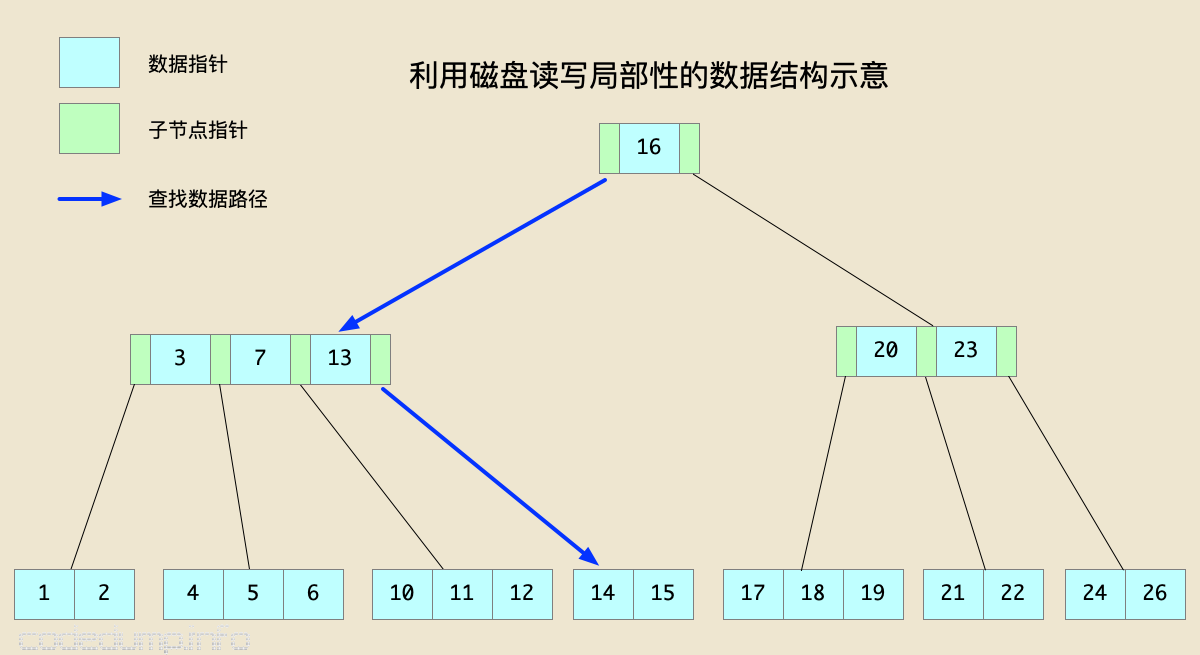
Commonly used data structures such as binary search tree (Binary Search Tree, BST) each node can only hold one data, resulting in a high tree height, the data of logically adjacent nodes may be far away, if in memory This is not a big problem for data manipulation in the middle, but because the speed of reading and writing to the disk is much slower than that of the memory, the unit of reading and writing to the disk each time is much larger than the smallest unit of reading and writing the memory.
Therefore, the corresponding data structure should meet the locality principle as much as possible, that is, when a piece of data is used, the nearby data will usually be used immediately. Therefore, logically adjacent data should be stored together as much as possible physically. , So as to reduce the number of read and write disks.
Therefore, compared with the BST data structure in which a node can only store one data, this data structure is required to be fatter and flatter in shape, that is, each node can hold more data, which can reduce the tree’s size. At the same time, the adjacent data can be stored on the physically adjacent hard disk space as much as possible, reducing disk reads and writes.
B-tree and B+-tree are two tree structures optimized by the principle of disk locality.
Click here to see more information about the post.